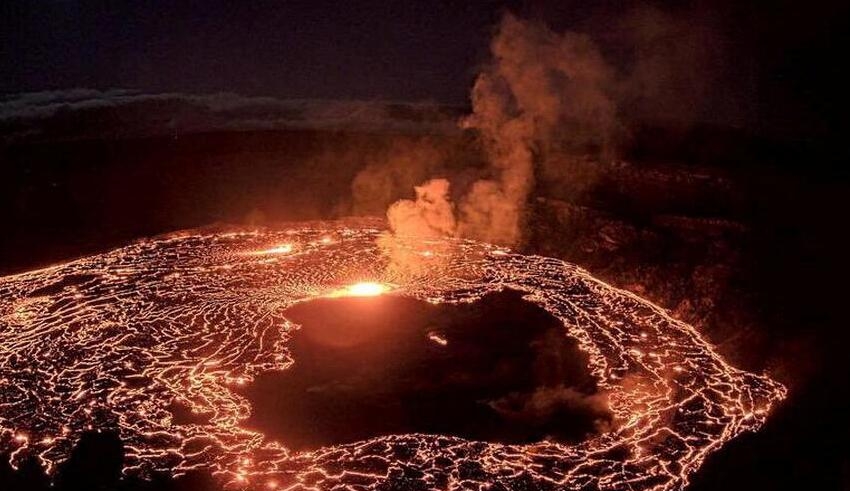
The United States Geological Survey reported that the Kilauea volcano in Hawaii started erupting on Thursday, January 5, after detecting a glow in the summit producing smog that is confined within the Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. This was stated in the volcanic activity notice issued by the US Geological Survey.
The warning stated that the alert level for the volcano was elevated to “Red” after an assessment of the eruption and the threats that were linked with it.
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) stated that the volcanic gas, which is composed of sulphur dioxide and other gases, has the potential to form a visible haze of volcanic smog, which is known as “vog,” and has been noticed in the region that is downwind of Kilauea.
Keep Reading
Vog has the ability to generate airborne health problems for inhabitants and visitors, causing breathing difficulties and also hurting agricultural crops. This is because of the fog’s potential to generate particulate matter.
Kilauea, which is known to be the younger and more active neighbor of Mauna Loa, which erupted in November for the first time since 1984, has been actively erupting since 2021. Mauna Loa also just experienced an eruption for the first time since 1984.
According to the USGS, the eruption of Mauna Loa has had no effect and the volcano is still calm.